FinTech – Financial technology is the intersection of technology to deliver financial services such as software to manage financial accounts, make payments or transfer money using smartphones and using analytics to make investment decisions.
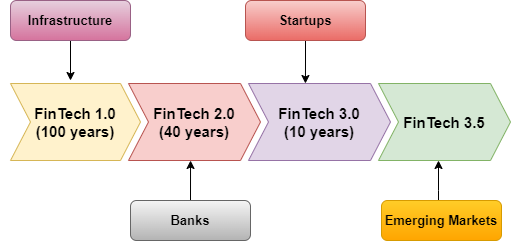
The Evolution of FinTech
- FinTech 1.0 : Infrastructure
- FinTech 2.0 : Banks
- FinTech 3.0 : Startups
- FinTech 3.5 : Emerging Markets
FinTech 2.0: Banks (1967)
- Evolution of finance and technology
- First automated teller machine (ATM)
- First handheld calculator
- Process of digitization
- Establishment of a series of domestic and international electronic payment systems in the late 1960s and early 1970s
- Establishment of NASDAQ the world’s first electronic stock exchange in 1971
- Online banking system in 1980
- Program Trading in 1987
FinTech 3.0: Startups and FinTech 3.5: Emerging Markets
- Global financial crisis – 2008 (real estate market crash)
- Blockchain – crypto and bitcoin
- Distributed ledger technologies
- Peer-to-peer landing
- Crowdfunding
- Mobile payment with Smartphones
How 2008 Impacted the development of FinTech?
- Unemployment
- Regulatory changes
- Distrust in Bank
- Invention of Smartphones – launched in 2007
FinTech Typology
- Finance and Investment
Alternative to Financing: Crowdfunding, P2P Lending, ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings)
- Operations and Risk Management
Pre 2008 financial crisis the focus was on Quantitative Risk Modelling Techniques eg. VAR (Value-at- Risk Systems) and after 2008 the financial services spend heavily on IT.
- Payments and Infrastructure
Electronic payments
- Data Security and Monetization
Datafication such as Big Data or Artificial Intelligence and Risk such as Hacking and Cyber Security
- Technology in the Customer Interface
New business technologies
Four Phases of Money
Barter System
In the 9000BC to 600BC with the limitations of the capacity of carrying goods, transporting it across long distance to make exchanges and standardize commence.
Commodity Money
In 1100BC, China used small bronze replicas of goods as token, while some countries also used silver and gold. In Rome, soldiers were paid in salt as their salary.
Coinage
Coinage was the system of creating and issuing coins as a form of currency. The coinage system was introduced by Lydians, currently known as Turkey around 600BC. China introduced paper money in 700AD and Europe did likewise in the year 16000AD
Dematerialized Payments
In the 1950s as the technology advanced and became more widely available, digital payments became more common and the volume of non-cash transaction has been steadily increasing ever since then.
Payment Evolution
- 1946 – Credit Cards
- 1950 – Cheques
- 1980 – ATM
- 1990 – EMV Standards
- 2000 – Mobile money, e-wallets and virtual cards
- 2009 – Bitcoin
- 2010 – Contactless Cards
- 2015 – Wearable devices, mobile wallets, other cryptocurrencies
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
Real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems enable the immediate exchange of large amounts of money between banks. These systems, which are often run by central banks or other financial institutions, are used for high-value transactions. Large sums of money may be transferred quickly and reliably between financial institutions because to RTGS systems’ rapid, secure, and effective architecture. RTGS systems are used to settle a variety of transactions, such as large-value business payments, government securities settlements, and interbank transfers. This is only possible because of technological capacities and customer expectation of instant delivery.